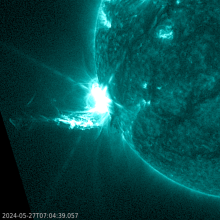
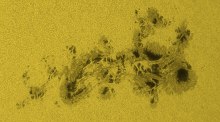
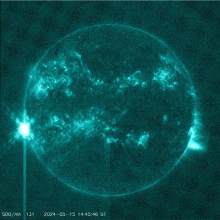
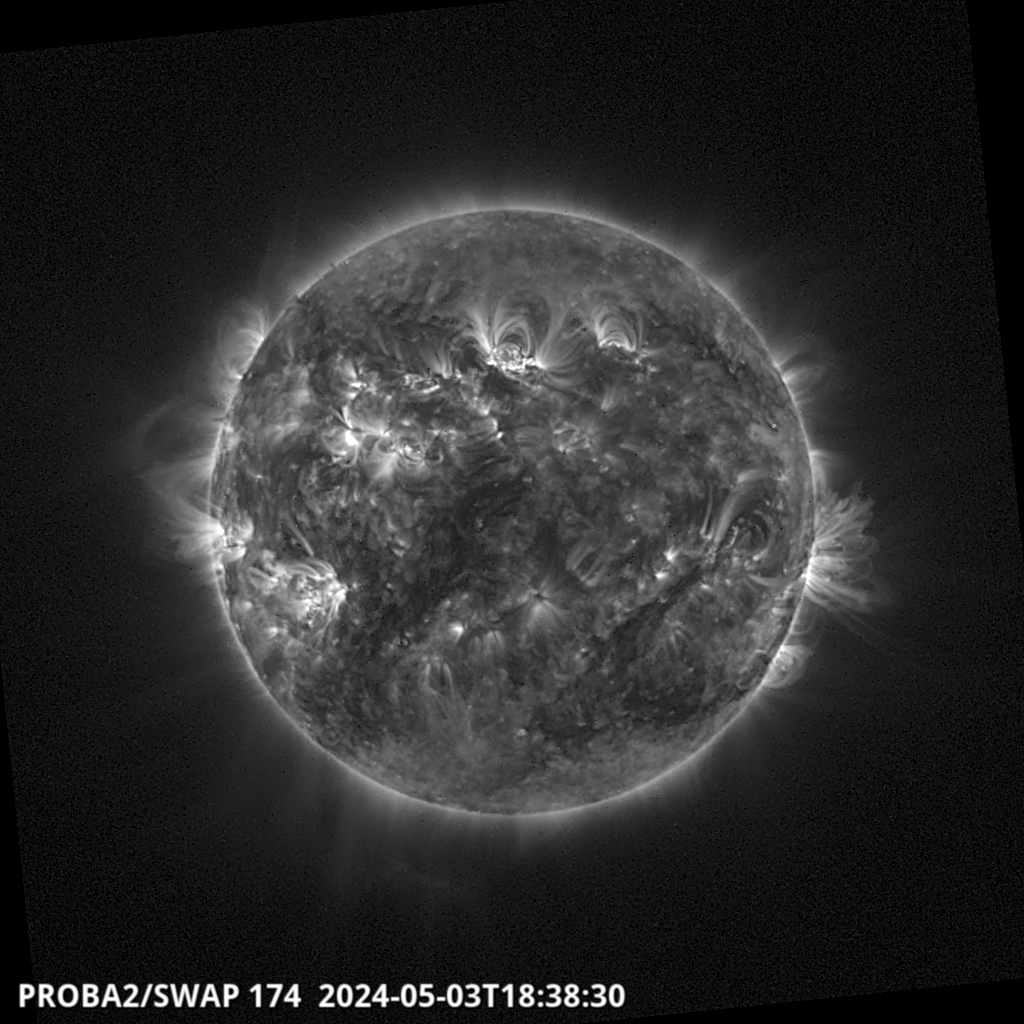
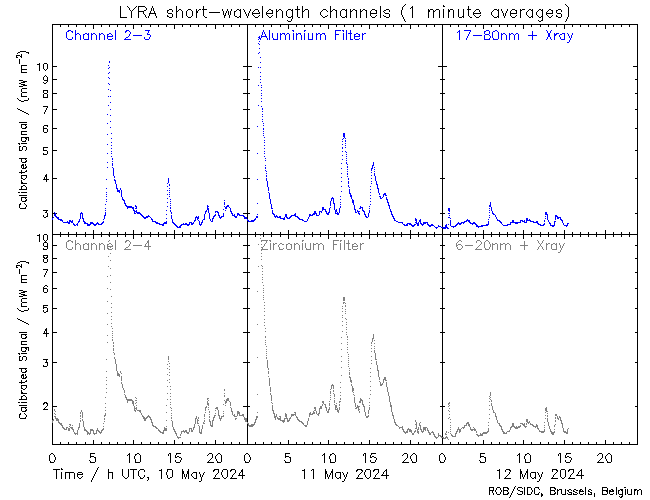
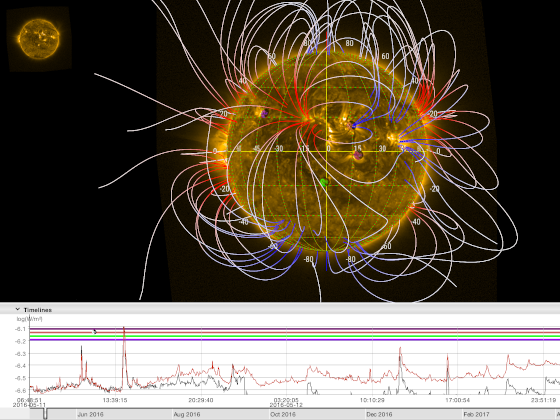
There are seven visible ARs on the solar disk. Solar activity has been high over the last 24 hours. The largest flare of the period was an X2.8 flare, with peak time 07:08 UTC on May 27. This flare originated beyond the south-east limb and is likely associated to a returning active region from the last rotation (NOAA AR 3664). Associated Type II and Type IV radio emissions were observed starting at 06:59 UTC and 07:05 UTC, respectively. Currently, NOAA AR 3691 is the most complex region on disk (beta-gamma-delta magnetic field configuration) and produced C-class flaring. The solar flaring activity is expected to be moderate over the next 24 hours with C-class flares expected, M-class flares likely and a low probability for further X-class flares, particularly from the expected returning active region that is about to rotate onto the disk.
No Earth directed Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) have been detected in the available coronagraph imagery. The CME related to the X2.8 flare will be analysed when data becomes available, however, due to the location of the flaring region any CME is not likely to have a strong Earth directed component.
Over the past 24 hours the greater than 10 MeV GOES proton flux was below the 10pfu threshold. There is a slight chance that the proton flux may increase in response to further strong flares.
The greater than 2 MeV electron flux increased slightly but remained below the 1000 pfu threshold as measured by GOES 16. It is expected to remain below this threshold over the next days. The 24-hour electron fluence was at nominal levels. The electron fluence is expected remain at nominal levels over the next day.